Indexes can be implemented using balanced trees, B+ trees, and hashes
Type of index:
Primary Index Fussy Index reversed index GSI LSI
@startuml
class IntColumnDataType{
min_value
max_value
void validate(value)
}
class StringColumnDataType{
min_value
max_value
void validate(value)
}
ColumnDataType <|-- IntColumnDataType
ColumnDataType <|-- StringColumnDataType
class ColumnDataType{
String type
void validate(value)
}
class ColumnSchema{
ColumnDataType type
String name
required
void allowNull()
void validateValue()
}
ColumnDataType -->ColumnSchema
class TableSchema{
schema_members
allow_undefined
validate_row_data()
}
ColumnSchema -->TableSchema
class Index{
index_name
primary_key
}
class Table{
table_name
table_schema
indexes
primary_key
table_data
}
Table *-- TableSchema
Database *-- Table
Table *-- Index
class Database{
db_name
tables
create_tables()
delete_tables()
}
@endumlTableSchema
validate_row_data(){
validates row data
Multi level validation
TableSchema : validates any undefined values
SchemaMember : validates null check
Column_data_type: validates value type and ranges.
}
-
ColumnDataType class: This includes different data types we can use for our columns. Here we can also have custom validations on each of the datatypes.
-
SchemaMember class: This is the actual column that our table schema would use. Here we can define the column name, type, and different validations on the column like null allowed, required or not, etc.
-
TableSchema class: This is the schema that will be used by the table to validate and store each row. Here we can define all schema members and validation methods as well.
SchemaMember def validate_value(self, val){
//validates column value
if val is None and not allow_none:
raise InvalidValueException(f"None_not_allowed_in_{self.column_name}")
return self.column_type.validate(val)
}
Index:
- Index class: This is the base for implementing different types of indexes defined by index_name and index_storage. Provides methods to index/query data and also to remove indexed value as well.
Reverse Index:
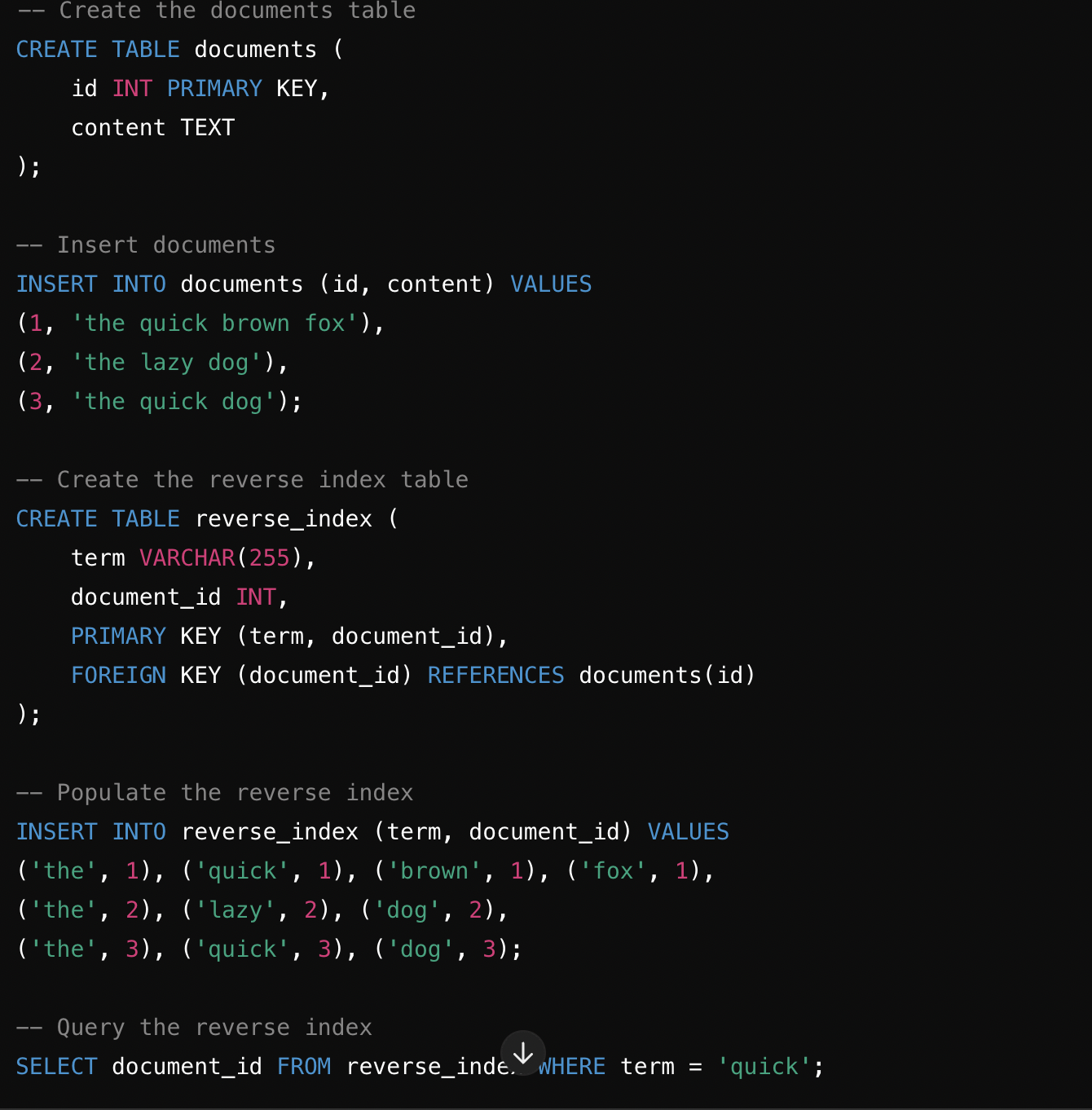
# create schema
user_schema = TableSchema()
user_schema.add_schema_member(SchemaMember("user_id", StrDataType(0, 10), required=True))
user_schema.add_schema_member(SchemaMember("user_name", StrDataType(0, 50)))
user_schema.add_schema_member(SchemaMember("user_age", IntDataType(0, 100), required=False))
# Create Table
user_table = Table(table_name="users", table_schema=user_schema, primary_key="user_id")
# create index
user_table.create_index("user_name", "FUZZY")
# insert seed data
user_table.insert_data({"user_id": "user1", "user_name": "new user", "user_age": 20})
user_table.insert_data({"user_id": "user2", "user_name": "improved user"})
user_table.insert_data({"user_id": "user3", "user_name": "diff guy", "user_age": 30})
print(user_table.filter_data({"user_name": "user"}))
# out : [{'user_id': 'user1', 'user_name': 'new user', 'user_age': 20},
# {'user_id': 'user2', 'user_name': 'improved user'}]
print(user_table.filter_data({"user_name": "user", "user_age": 20}))
# out : [{'user_id': 'user1', 'user_name': 'new user', 'user_age': 20}]
user_table.delete_data("user2")
print(user_table.filter_data({"user_name": "user"}))
# out : [{'user_id': 'user1', 'user_name': 'new user', 'user_age': 20}]