There are three ways a service can be discovered.
- Allow clients to contact any node (e.g., via a round-robin load balancer). If that node coincidentally owns the partition to which the request applies, it can handle the request directly; otherwise, it forwards the request to the appropriate node.
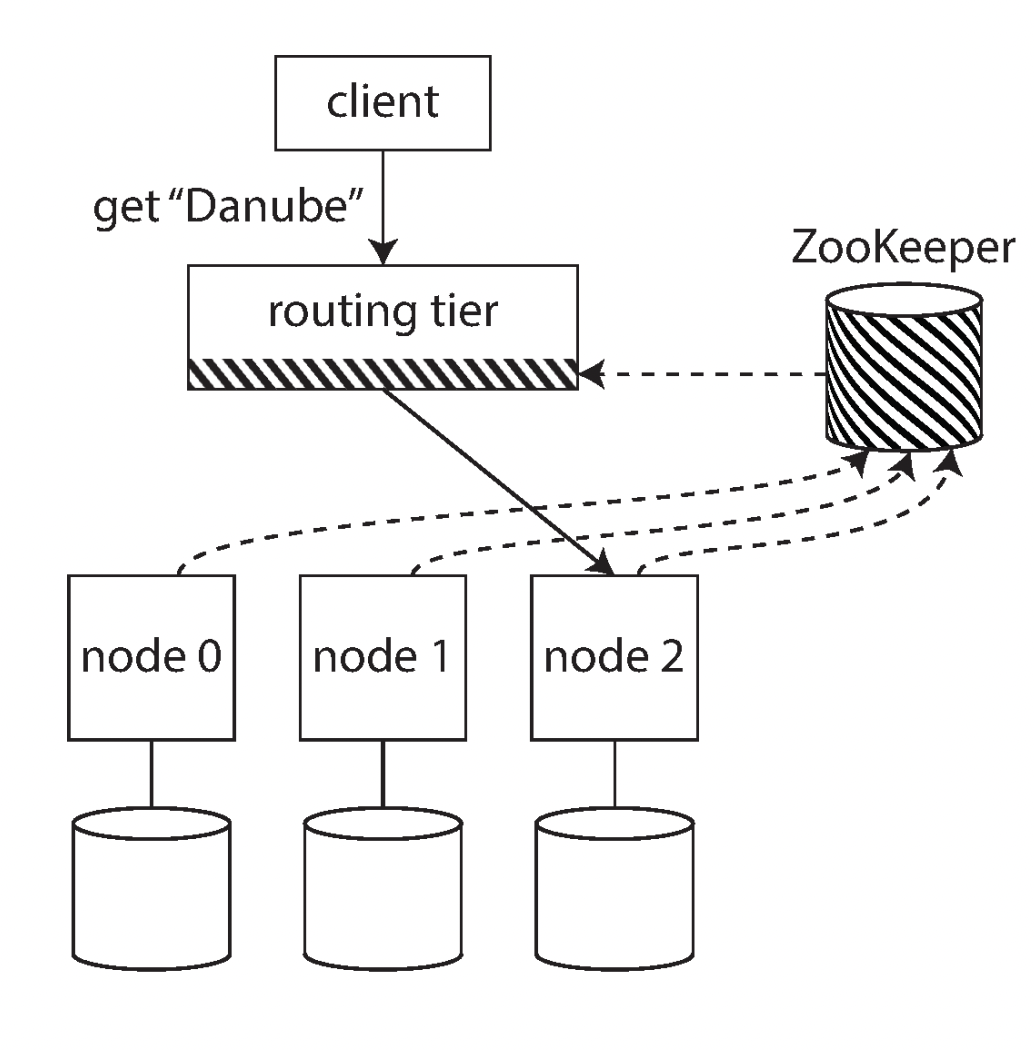
- Send all client request to routing tier, which determines which node the request should be handled and forward the request to that node.
- Client itself can be aware of the partitioning and assignment details and can directly connect to appropriate node.
Problem is how does the component weather nodes, client or routing tier be aware with the changes in assignment of partitions. it is important that all participants agree— otherwise requests would be sent to the wrong nodes and not handled correctly. There are protocols for achieving consensus in a distributed system, but they are hard to implement correctly.
Many distributed data systems rely on a separate coordination system such as Zookeeper. Zookeeper maintains and mapping of partitions to nodes.
Examples for coordination systems used in distributed systems:
- LinkedIn’s Espresso uses Helix
- HBase, SolrCloud, and Kafka also use ZooKeeper
- MongoDB uses config servers and mongos daemons.
- Cassandra and Riak take client forwarding approach: they use a gossip protocol among the nodes to disseminate any changes in cluster state, request can be forwarded to any node and that nodes forwards them to specific nodes for the requested partition.
- Couchbase does not rebalance automatically. it is configured with a routing tier called moxi, which learns about routing changes from the cluster nodes
Partitions details maintained by Nodes puts more complexity in the database nodes but avoids the dependency on an external coordination service such as ZooKeeper.
When using a routing tier or when sending requests to a random node, clients still need to find the IP addresses to connect to.These are not as fast-changing as the assignment of partitions to nodes, so it is often sufficient to use DNS for this purpose.