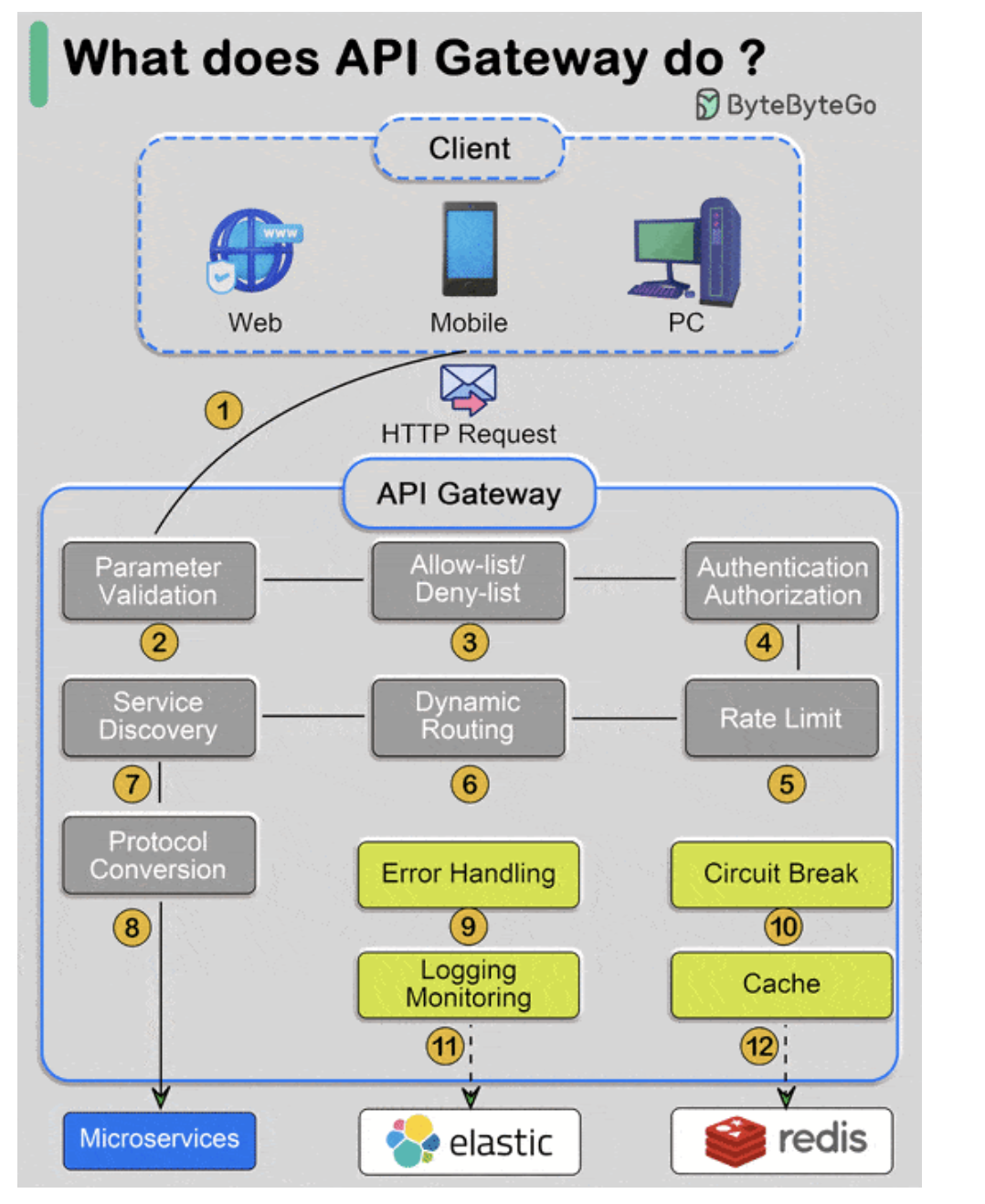
Steps:
2. Validate request parameters
3. check if the request is allowed or denied based on the request token and client
4. Check if the passed token can be authenticated and authorised to access the resource
5. Check if the limit is reached to access the resource by requested client
6. Figure out Dynamic routing based on based on Request Headers, request path, request method, body, query params, user attributes such as caller country.
Ex: e-commerce API Gateway might route requests based on the user’s country:
Extract Country: The gateway extracts the user’s country from the request headers (e.g., X-Country header).
Route Request: The gateway routes the request to the appropriate regional service based on the extracted country.
-
Service Discovery: - The API Gateway queries the service registry to obtain the current list of available instances for a particular service. The registry provides the API Gateway with the information to route requests to the appropriate service instances. It also uses different load balancing strategies such as round robin, least connection etc to distribute traffic effectively.
-
Protocol conversion: The API Gateway receives a request from a client. This request can be in any supported protocol, such as HTTP, REST, gRPC, or SOAP.