InfluxDB, Prometheus DB, TimeScaleDB, Timestream
Benefits of TSDB
- Performance: TSDBs are optimized to handle the ingestion, compression, and querying of time-series data. Traditional databases can struggle to process this data as efficiently.
- Data Volume: Time-series data can rapidly accumulate over time. TSDBs are built to handle this scale.
- Time-Centric Queries: If your application needs to perform queries that are oriented around time (e.g., what was the temperature of this device at time X, or how many users visited our site every minute for the past hour?), a TSDB makes this easy and efficient.
- Data Lifecycling: Often, time-series data is useful only for a certain period (like the last month or year). Beyond that, you may want to downsample or delete it. TSDBs often come with built-in support for this kind of data lifecycle management.
- Real-Time Processing: TSDBs are often used in scenarios where you need to ingest and query data in real time.
- Analytics and Trend Analysis: TSDBs typically support functions that allow you to do sophisticated trend analysis and forecasting on your time-series data.
- Anomaly Detection: Timeseries databases can help identify outliers or anomalies in your data, which can be critical for fields like fraud detection, system health monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
Components of a TSDB
- Data Ingestion Layer: This is responsible for accepting incoming data streams. It may be designed to handle large volumes of data at high velocity.
- Storage Engine: The heart of the TSDB, this component is responsible for storing the time-series data. It is optimized to handle time-series data efficiently, usually employing specific compression algorithms to reduce the amount of storage needed and to increase query speed.
- Indexing Mechanism: Given the large volumes of data that can be stored, a TSDB must have a robust indexing mechanism to enable efficient retrieval of data. The data is primarily indexed by time, but it may also be indexed by other fields or tags.
- Query Engine: This component allows users to retrieve and analyze data. The query language varies between different TSDBs. Some might use SQL-like syntax, while others have custom DSLs (Domain Specific Languages) designed to facilitate complex queries on time-series data.
- Data Retention and Downsampling Policies: These mechanisms define how data is aged out or reduced in granularity as it becomes older. This is crucial in managing the potentially massive amounts of data a TSDB can accumulate.
- High Availability and Fault Tolerance Mechanisms:
- Security
- APIs and Integrations:
- Administration and Monitoring Tools:
INFLUX DB
- DevOps Observability — Observing and automating key customer-facing systems, infrastructure, applications and business processes.
- IoT Analytics — Analyzing and automating sensors and devices in real-time delivering insight and value while it still matters
- Real-Time Analytics — Leveraging the investment in instrumentation and observability — detecting patterns and creating new business opportunities
- Ease of Scale-Out & Deployment — Millions of writes per second, and clustering to eliminate single points of failure.
- Quickly find value in data — control systems, identify patterns, and predict the future.
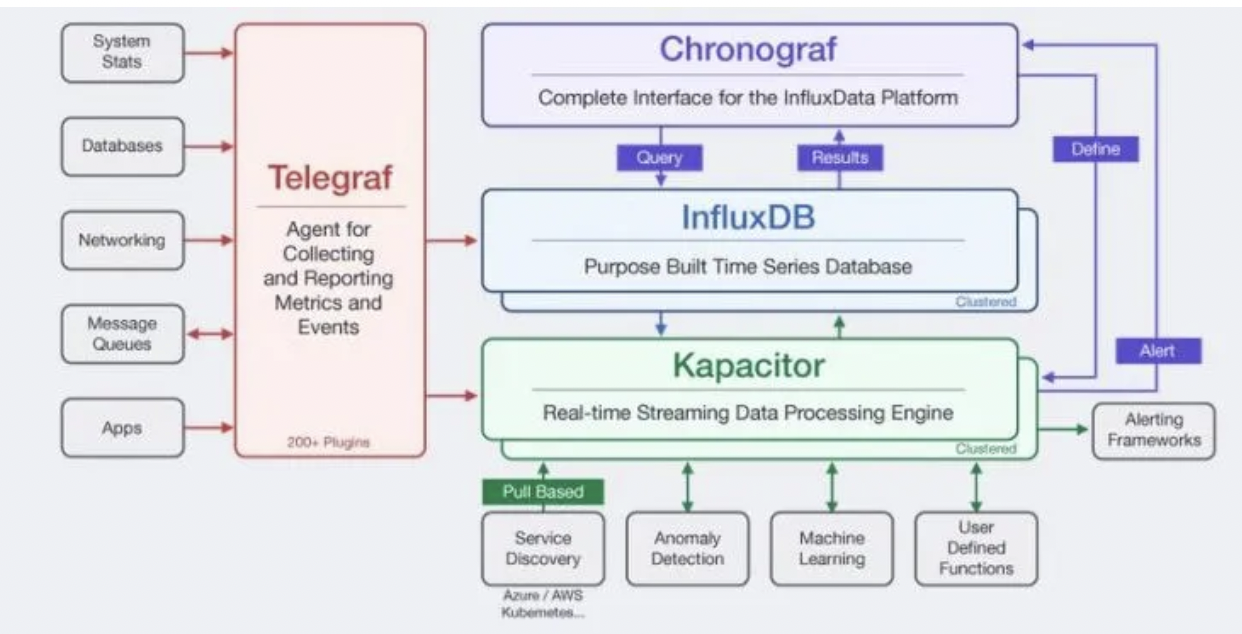
Open Source Time Series Platform
The InfluxData Platform is built upon a set of open source projects, which are collectively called the TICK Stack. Below, learn more information about Telegraf, InfluxDB, Chronograf, and Kapacitor and their specific functions within InfluxDB’s open source core.
Each datapoint is associated with time when it was recorded in a timeseries date

Other example of Time series of data
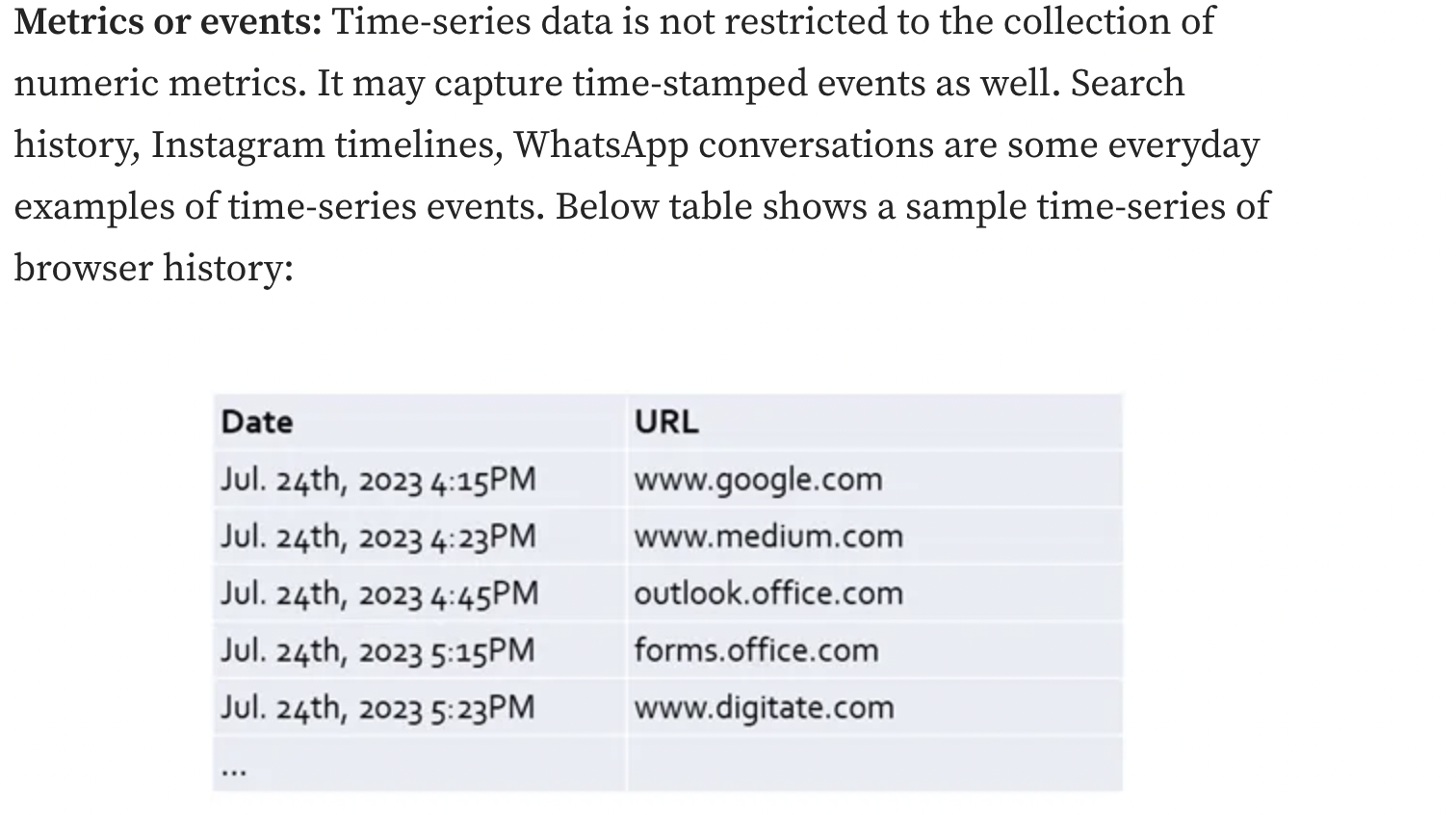
NOTE: time series data is its immutability; once recorded, it generally remains unchanged. The price of Google stock from a week ago will always be the same
-
Immutable data over time
-
Each data point exists in relation to a timestamp
-
Timestream: Developed by Amazon Web Services (AWS), Timestream is a fully managed time series database designed for handling large-scale, high-resolution data. It integrates well with other AWS services, offers built-in time series functions, and provides easy data ingestion and querying capabilities.