Design payment system for global payments for users and merchants.
Payment Gateways: A secure systems between client app and bank for processing transactions.
transfer payment data from users to payment processor
Payment Processors:
it communicates with banks and card networks like visa and master card. it ensure transfer of money from user account to merchant account.
Requirements:
Type Support one time payment Recurring payments like subscriptions Refunds Dispute resolutions Currencies: Multiple currencies Real time exchange rates Volums: 1k/txn per sec follow regulations like KYC, and PCI
NFR:
1k of txn/sec ACID compliemence consistency across distributed systems Heigh reliability: 99.99% availabliity top notch security scalability : Scalable at Global level low latency Extensible for additional currencies and payment methods(like UPI, light UPIs)
Databases:
Sql DB for ACID complience
User: name userid ( shard based on userid or regions ) password profile data kyc(know your customers) status created at
Payment table payment request id userid merchantid amount currency code payment method (paypal/credit/debit/netbanking) requesttime status ( success/failed/pending)
Currency Exchange rates table exchange rate id source currency target currency rate last updated
Transaction txnid accountid account currency status createdat
Fraud Detection Table ( can be used by LLM service ) id txn Id user id suspecioud activity ( unusual location / multiple failed login / large txn size ) fraud score action taken ( held payment / failed payemnt / declied payment )
Notification tables id userid type ( email / sms) message delivery status timestamp
No Sqls
session details id userid login time ip address device { type, os, browser } jwt token expration time
Event logs id event type ( user login / txn completed) user id timestamp details{ type, os, browser or txnid currency id payment method amount }
Kafka Queues:
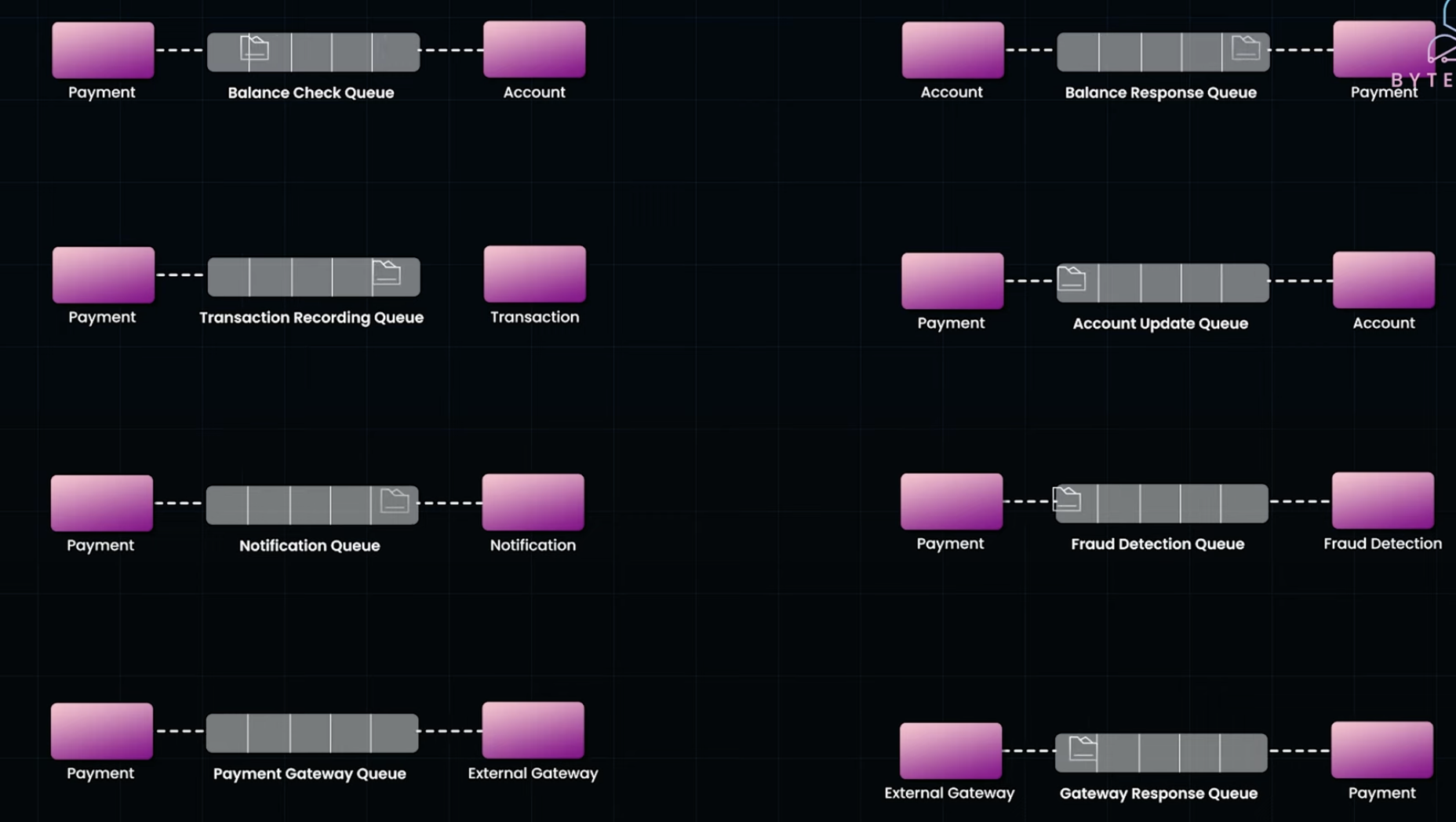
Patterns
Circuit breaker while external communication Saga patterns ensure ACID in distributed systems between multiple services in distributed systems. Retry failing handling Idempotent keys unique keys
Security
User athentication Data encryption No PII data leak access authurisation role based access, multifactor auth fraud detection
Encryption in Transit:
- TLS/SSL:
All communication between payment terminals, mobile apps, and backend services is typically secured using TLS (Transport Layer Security) to prevent eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. - VPNs:
In some cases, virtual private networks (VPNs) are used for secure communication between different network segments. Encryption at Rest: Symmetric Encryption:
Sensitive data stored on disk, such as cardholder information or transaction logs, is encrypted using symmetric encryption algorithms (e.g., AES-256). This ensures that even if storage is compromised, the data remains unreadable without the proper keys.
Tokenization and Data Masking
Tokenization: Instead of storing sensitive payment data (e.g., credit card numbers), tokenization replaces it with a surrogate value (token) that has no exploitable value if breached
Data Masking:
When sensitive data must be displayed (for example, in a user interface), data masking techniques are applied so that only non-sensitive portions are visible.
Authentication and Authorization 2FA Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Strong Password Policies & Token-Based Authentication:
The network is protected by firewalls, IDS/IPS systems, and regular vulnerability scanning, while all application-level activities are logged for audit purposes.