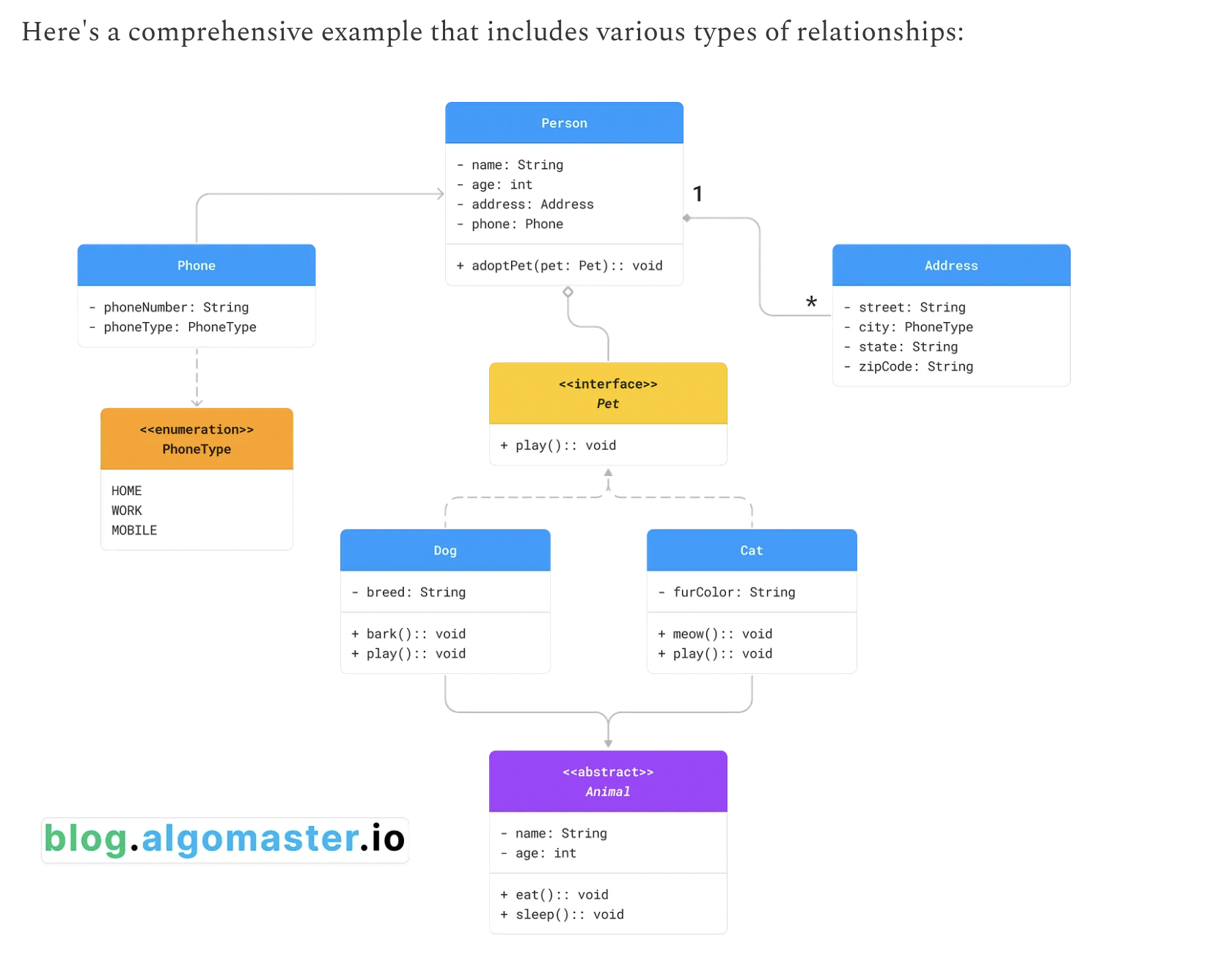
. Association
Association represents a “uses-a” relationship between two classes where one class uses or interacts with the other.
Example: A Student class is associated with a Course class, as a student can enroll in multiple courses.
2. Aggregation
Aggregation represents a “has-a” relationship where one class (the whole) contains another class (the part), but the contained class can exist independently.
Example: A Car class has an Engine class but the Engine class can exist without the Car class.
3. Composition
Composition represents a strong “has-a” relationship where the part cannot exist without the whole. If the whole is destroyed, the parts are also destroyed.
Example: A House class is composed of Room class but the Room class can not exist without the House class.
4. Inheritance
Inheritance (or Generalization) represents an “is-a” relationship where one class (subclass) inherits the attributes and methods of another class (superclass).
Example: A Dog class and a Cat class inherit from an Animal class, as both dogs and cats are animals.
5. Dependency
Dependency represents a “uses” relationship where a change in one class (the supplier) may affect the other class (the client).
Example: A Customer class uses an Order class to place order.