Eviction strategies
- Least Recently Used (Jump to head on access)
- Least Frequently Used
- FIFO
- LIFO
- A hybrid algorithm
Requirement:
store different data sets fetch data by key remove value from cache by TTL remove value from cache based on eviction policies
NFR:
concurrency latency search in O(1) save in O(1)
What data structure and algo we can use doubly linked list + Hashmap and use evicition policy as LRU. that is also an Linked Hash Map
cache-dig
⚠ Switch to EXCALIDRAW VIEW in the MORE OPTIONS menu of this document. ⚠ You can decompress Drawing data with the command palette: ‘Decompress current Excalidraw file’. For more info check in plugin settings under ‘Saving’
Excalidraw Data
Text Elements
head
tail
1
2
3
4
101
102
103
104
1
101
2
3
103
4
104
102
Link to original
call for get(3) then tail will contain 3, as tail is keeping the least recently used call to add new element 10, but size of the cache is 4 only, and its full. 10 will be set as tail and head will be shifted to next position new entry will be added in hashmap, and old head entry will be removed from map call to remove (2) remove 2 node from DDL remove 2 from hashmap
Sudocode:
```public class Cache{
private CacheStorage storage;
private EvictionPolicy ePolicy;
cache(EvictionPolicy ePolicy, CacheStorage storage )
{
this.storage = storage;
this.ePolicy = ePolicy;
}
public String get(String key)
{
this.ePolicy.keyAccessed(key);
return this.storage.get(key);
// fetch from storage map
// call keyAccessed
}
public void put(String key, String value){
this.storage.put(key, value);
// check if key not present in storage map
// check if size is not reached, else call evict()
// create DDL node, insert in map
// move it to tail using keyAccesssed()
}
}
public Interface EvictionPolicy{
keyAccessed(String key);
evict();
}
public Interface CacheStorage {
public String get(String key);
public void put(String key, String value);
}
public DDLNode{
String next;
String prev;
String data;
}
public DDL{
private DDLNode head;
private DDLNode tail;
public DDLNode getHeadNode();
public DDLNode getTailNode();
public DDLNode getNodeAtEnd();
public DDLNode inserthNodeAtEnd(key);
public void DetatchNode(DDLNode node);
}
public class LRUEvictionPolicy{
private Map<String,DDLNode> evictionNodeMap;
private DDL ddl;
keyAccessed(String key){
// move key node to tail
if(evictionNodeMap.containsKey(key)){
ddl.detatchNode(evictionNodeMap.get(key));
ddl.attachAtEnd(evictionNodeMap.get(key));
}else{
DDLNode currentNode = ddl.attachAtEnd(key);
evictionNodeMap.put(key, currentNode);
}
}
public String evict(){
// remove head element
DDLNode head = ddl.getFirstNode();
if(head == null)
return;
else{
ddl.remove(head);
evictionNodeMap.remove(head.data);
return head.data;
}
}
}
public class MapCacheStorage {
private int size;
private Map<String, String> storage;
public String get(String key){
if(!storage.contains(key)){
return null;
}else
return storage.get(key);
}
public void put(String key, String value){
if(!isFull())
storage.put(key, value);
}
MapCacheStorage(int size){
this.size;
}
public String remove(String key){
if(!storage.contains(key)){
// throw key not found;
}else
return storage.get(key);
}
private boolean isFull(){
return storage.size()==size;
}
}
psvm(){
Cache cache = new Cache(new MapCacheStorage(10), new LRUEvictionPolicy());
cache.put();
cache.put();
cache.put();
cache.remove();
cache.get(key);
}
Cache with LFU eviction policy
Using Min Heap
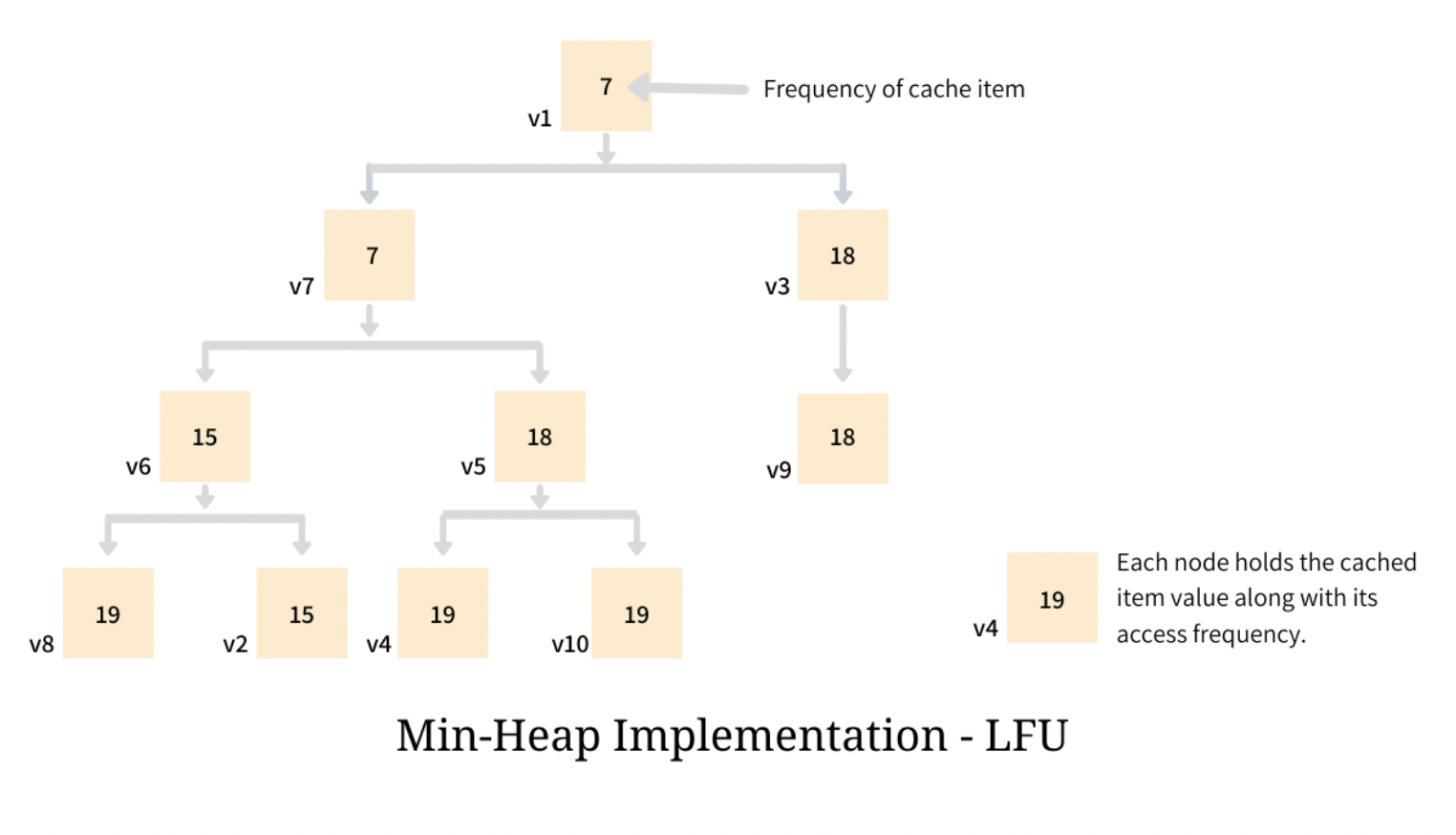
Although the identification of the element to be evicted is quick, but in order for the heap to maintain its property - element with lowest access frequency be at the top - it demands a rebalance, and this rebalancing process has a running complexity of O(log n). To make things worse, rebalancing is required every single time the frequency of an item is changed; which means that in the cache that implements LFU, every time an item is either inserted, accessed or evicted, a rebalance is required - making all the three core operations to have the time complexity of O(log n).
Using DoublylinkedList
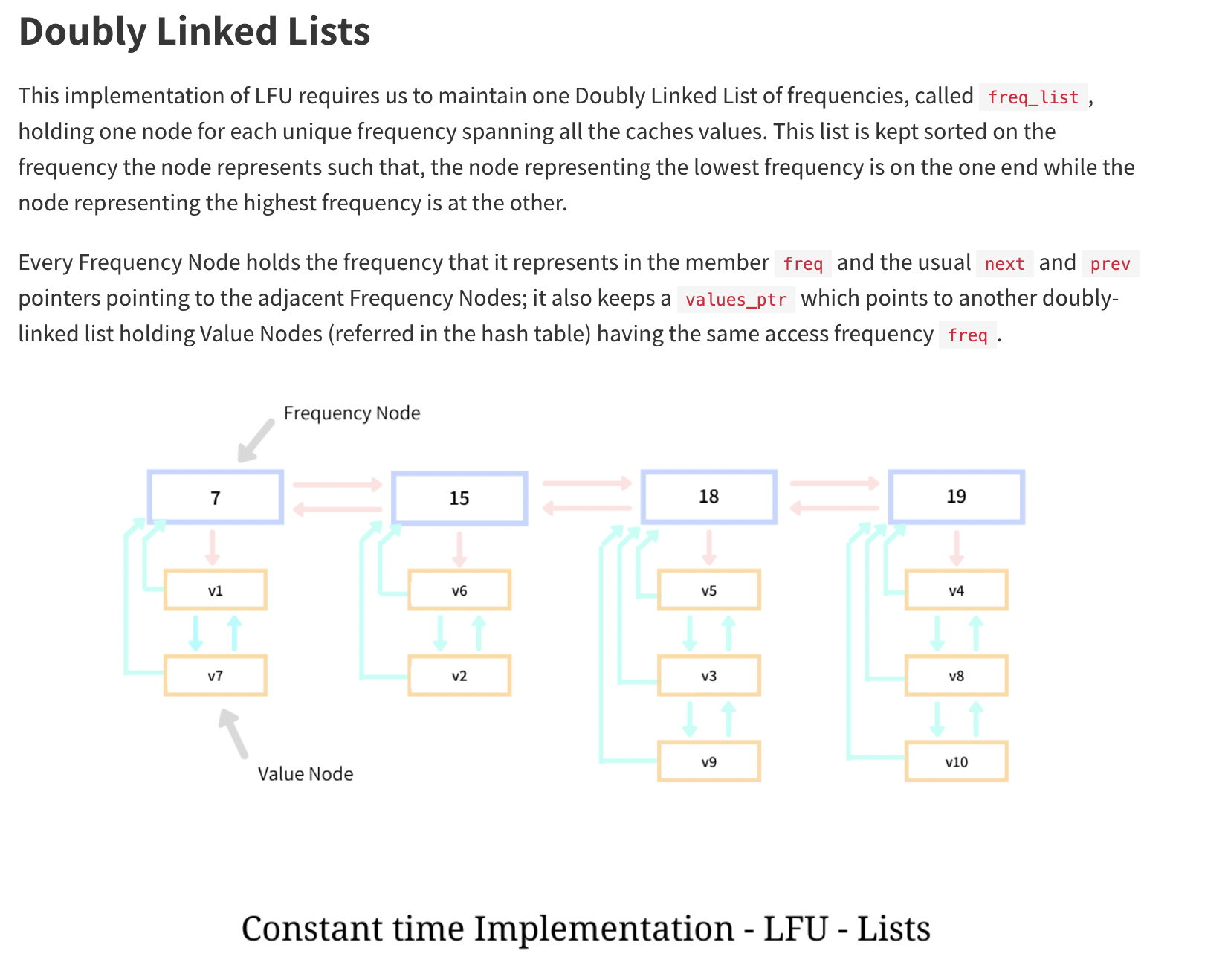
https://www.enjoyalgorithms.com/blog/least-frequently-used-cache